With the emerging high-speed network standards and rapidly advancing technology, fiber optic network is driven to meet the growing demand for faster access to larger volumes of data. Although 10G/40G Ethernet becomes the mainstream of telecommunication market nowadays, organizations of all sizes still need to be prepared to integrate speeds of 100G and beyond. For data center networking, users can choose different solutions based on the different transmission distance need. In general, there are two kinds of 100G fiber optic solutions: direct cabling and breakout cabling. It is essential for users to understand the detailed information of each type of solution in order to select the one that meets their current and future connectivity needs.
How 100G Optics Develop
After the IEEE completing the certification of the first 100G standard for Ethernet networks, the transceiver industry launched a new type of form factors for 100G connectivity—CFP ("C" for 100, and FP for Form factor Pluggable). Compared to the most popular 40G QSFP, the size of CFP transceiver is huge. And most CFP implementations doubled the power consumption per bit. Furthermore, the price per bit increased by a factor of ten. These disadvantages becomes the main obstacles of the popularity of 100G CFP transceivers.
The next version of 100G form factors is the CFP2, CFP4, and the CPAK that are improved upon the CFP. But when compared to the popular 10G SFP+ and 40G QSFP+, none of these new members of the CFP family improved density, power consumption, or cost. Fugure 1 shows the size comparison between CFP2, CFP4 and QSFP28 modules.
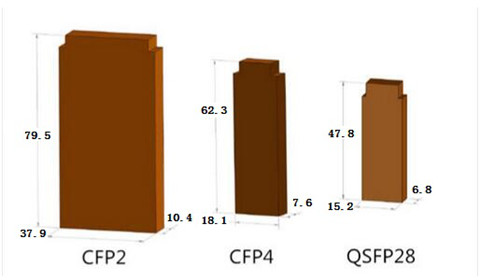
Then here came the 100G QSFP28. The QSFP28 is the exact same footprint as the 40G QSFP+. The 100G QSFP28 is implemented with four 25-Gbps lanes, Just as the 40G QSFP+ is implemented using four 10-Gbps lanes. In all QSFP versions, both the electrical lanes and the optical lanes operate at the same speed, eliminating the costly gearbox found in CFP, CFP2, and the CPAK. The 100G QSFP28 makes it as easy to deploy 100G networks as 10G networks. When compared to any of the other alternatives, 100G QSFP28 increases density and decreases power and price per bit. That’s why it is fast becoming the universal data center form factor. The following part will move on to talk about the 100G optic cabling solutions.
100G Direct Cabling Solutions
QSFP28 transceiver utilizes either fiber or copper media to achieve 100GbE communication in each direction. This transceiver has 4 individual 25GbE lanes which can be used together to achieve 100GbE throughput or separately as 4 individual 25GbE connections (using 4 SFP28 modules).
For 100G short-reach direct cabling within 100m, 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 optical module and 100G QSFP28 cable are good choice. Just from the table list of 100G optical modules and cables, we know that 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 modules can support up to 100 m on OM4 12 fiber multimode MTP cable. And 100G QSFP28 to QSFP28 direct attach copper cable can support up to 5m and 100G QSFP28 to QSFP28 active optical cable can support up to 10m. Figure 2 describes a 100G direct cabling with the use of QSFP28 to QSFP28 DAC and AOC cables.

For 100G long-haul direct cabling, like 10km, both 100GBASE-LR4 QSFP28 optical module and 100GBASE-LR4 CFP4 transceiver can support up to 10km on single-mode LC patch cables. For longer 100G direct cabling above 10km, the 100GBASE-ER4 CFP is the ideal choice as their transmission distances support up to 40 km.
100G Breakout Cabling Solutions
A breakout cable is a multi-strand cable, typically custom-made, which is divided into multiple duplex cables. For instance, a 40G breakout cable has four individual 10G duplex cables totaling eight strands, while a 100G breakout cable has 10 duplex cables and 20 strands. Figure 3 displays a simple 100G connectivity with 100GBASE-SR4 QSFP28 and QSFP28 to 4SFP28 breakout cables.

Between the 100G optical module and 25G optical modules, there always uses the breakout cables connected the two kinds of optical modules, and the common cable solutions are 100G QSFP28 to 4SFP28 Breakout AOC cables or 100G QSFP28 to 4x 25G SFP28 Breakout Direct Attach Passive Copper Cables.
The commonly used 100G breakout cabling solutions is 100G QSFP28 to 4SFP28 DAC. It’s easy to understand how this type of cable function. Just as the QSFP+ breakout cable, the 40GBASE-SR4 QSFP+ optical module at the one end can be connected to 4x10GBASE-SR SFP+ optical modules at the other end.
Conclusion
As IT infrastructures are planning to migrate to 100G data rate, network designers must carefully weigh alternative implementations of such links. With a variety of fibers already deployed, it is important to understand the interoperability of new optics with existing fibers. And for 100G deployment, you are supposed to understand the benefits and challenges of each type of the fiber optic solutions before taking an action. FS.COM’s 100G FHD series covers a full range of 100G optical transceivers and cables, like CFP, CFP2, CFP4, QSFP28, as well as 100G QSFP28 to QSFP28 DAC, 100G QSFP28 to 4SFP28 DAC. Besides the above products, 100G FHD Fiber Enclosures, 100G FHD MTP Modular Cassettes, 100G 160 Fiber 2U Panels and 100G CFP SR10 Cables are also provided.
评论
发表评论