HFC is short for Hybrid Fiber/Coax. This network can provide reliable bandwidth for all types of interactive video, data, and voice services. HFC, as an advanced community antenna television (CATV) network, is not hampered by the same copper wire restrictions as ADSL. Traditional cable technology is a one-way broadcast system. The technical challenge of this network is not in getting the throughput but in achieving two-way communication The present article shows how the HFC access network interconnects them, both for user and signaling data.
HFC—Definition and Its Working Principle
HFC refers to a broadband telecommunication network that combines optical fiber and coaxial cable, which has been utilized globally by cable television operators since the early 1990s. HFC is also called the 2nd generation of CATV systems that use fiber optic cable for the headend and feeder distribution system and coax for the customers end connection. HFC system is mainly used for delivering video, telephony, voice telephony, data and other interactive services over coaxial and fiber optic cables. In a HFC system, the fiber optic network extends from the cable operators’ master headend, then out to a neighborhood’s fiber hub, and finally to a coaxial fiber node which serves anywhere from 25 to 2000 homes.
HFC refers to a broadband telecommunication network that combines optical fiber and coaxial cable, which has been utilized globally by cable television operators since the early 1990s. HFC is also called the 2nd generation of CATV systems that use fiber optic cable for the headend and feeder distribution system and coax for the customers end connection. HFC system is mainly used for delivering video, telephony, voice telephony, data and other interactive services over coaxial and fiber optic cables. In a HFC system, the fiber optic network extends from the cable operators’ master headend, then out to a neighborhood’s fiber hub, and finally to a coaxial fiber node which serves anywhere from 25 to 2000 homes.
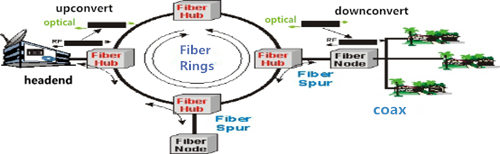
The above image shows HFC distribution system. Firstly, multiple RF television channels at the headend are shifted in frequency to allow distribution through high-speed fiber cable. The fiber cables are connected in a loop around the cable television service area. In this way, if any break occurs in the cable, the signal will automatically be available from the other part of the loop. The loop is tapped at regular points by a fiber hub that can distribute the optical signals on fiber spurs. At last, the fiber spurs end into fiber nodes that translate the signal from a light beam to an electrical signal, and send it over coaxial cable lines for distribution to subscriber residences.
Significant Benefits—HFC Over CATV
To begin with, HFC network provides high performance at low cost because they can be designed to match the asymmetrical bandwidth needs of most broadband distribution systems. In addition, it needs less maintenance costs due to fewer amplifiers required and also less electricity than coaxial.
To begin with, HFC network provides high performance at low cost because they can be designed to match the asymmetrical bandwidth needs of most broadband distribution systems. In addition, it needs less maintenance costs due to fewer amplifiers required and also less electricity than coaxial.
Next, compared to CATV, HFC network is more reliable, immune to noise and possesses almost non-existent attenuation. In addition, the other advantage of HFC is that there is no need to change the already existing coaxial networks as it uses a separate connection. It also has the ability to adapt to new services such as voice, data or video without changing existing operational parameters.
What’s more, HFC network possesses a high bandwidth capabilities. It increases from traditional CATV network (up to 330 MHz or 450 MHz) to 750 MHz (can be upgraded to 1 GHz in the future) with HFC. This new generation cable network is now used for cable telephones, increased number of CATV channels (to over 200) and a direct infrastructure to new digital TV standards.
Summary
HFC improves the quality of TV signal. At the same time, it can support high speed bi-directional data communication. HFC Network might be one solution of the bandwidth starvation in the future. Fiberstore offers a variety of optical communication products including HFC optical transmitter, HFC optical receivers, FTTH optical transmitter, FTTH optical receivers, SAT-IF optical transmitter and receiver, EOC system products, and optical switches, etc. They also have compatible Juniper QSFP+ modules (like JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 and JNP-QSFP-40G-LX4).
HFC improves the quality of TV signal. At the same time, it can support high speed bi-directional data communication. HFC Network might be one solution of the bandwidth starvation in the future. Fiberstore offers a variety of optical communication products including HFC optical transmitter, HFC optical receivers, FTTH optical transmitter, FTTH optical receivers, SAT-IF optical transmitter and receiver, EOC system products, and optical switches, etc. They also have compatible Juniper QSFP+ modules (like JNP-QSFP-40G-LR4 and JNP-QSFP-40G-LX4).
评论
发表评论