As the optical technology grows more sophisticated and expand into high bandwidth optical backbone connectivity, enterprises are now turning to the private and secure dark fiber network. By leasing dark fibers, network operators can cut down the labor cost of developing fiber networks. What’s more, enterprises can use their own optical technician and networking equipment to connect multiple locations to create a private network or to connect to other network hubs to gain access to various high speed internet. So what exactly is dark fiber? Is it the dark side or the right side of a fiber optic network? Here are a few things you should keep in mind.
What Is Dark Fiber?
Dark fiber refers to the optical fiber that has not been used but available in fiber optic communications. The dark cable is composed of hundreds and thousands of fiber jumper cables carrying high amounts of data at high speeds over hundreds of miles. Network operators originally used the term—dark fiber to describe the potential network capacity of telecommunication infrastructure, but now also refer to the increasingly common practice of leasing fiber optic cables from a network service provider, or the fiber installations not owned or controlled by traditional carriers. Dark fiber is capable of supporting unlimited data rates and possess the overcapacity just as listed below:
- Unlimited bandwidth when fiber is used in conjunction with WDM
- Long-term fixed costs to ease financial planning issues
- The ability to centralize IT assets in central offices, head ends and data centers
- Significantly reducing active components in the network thereby lowering maintenance costs
- The ability to easily connect to other service providers which lowers costs and increases coverage
- The ability to reach new customers and generate new service revenue
Dark Fiber Networks Solution
In contrast to the traditional fiber network, a dark fiber network is a privately operated optical fiber network separate from the main network and is controlled by the client rather than the network provider. Dark fiber networks can be set up in a variety of ways, including dark fiber rings, point to point or point-to-multipoint configurations.
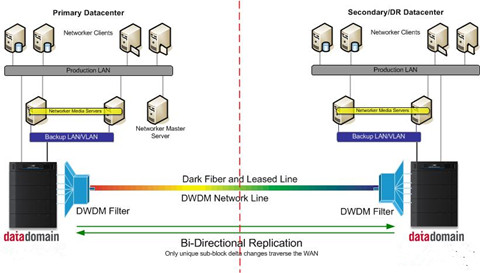
A dark fiber network requires less power and has a higher capacity, generally due to the use of DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing). Simply put, with DWDM, dark fiber network can easily increase bandwidth and allow more data to be send via optical fibers. Furthermore, dark fiber often has better signal strength and is more immune to interference than the fiber making up traditional networks. The image above shows how we can use dark fiber as the carrier medium and can achieve multiple channel traffic with DWDM as a termination point.
Why Dark Fiber?
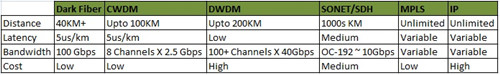
If your company is considering utilizing a dark fiber network, there are a few things you should bear in mind. First, make sure you buy dark fiber for the right reasons. Most companies adopts a dark fiber network because of the premium advantage of the service itself—unlimited, scalable bandwidth. By the utilization of dark fiber, enterprises can upgrade bandwidth they need by changing out equipment interfaces themselves, without notifying carrier or worrying about term liability on a leased circuit. That’s a good option for companies whose bandwidth needs can change rapidly or unpredictably for point to point connectivity. Furthermore, with dark fiber, a client can expect to get high levels of performance, a highly secure network and superfast speeds just as you can see in the following chart.
But buying dark fiber is not like buying other telecom services because it’s more like a physical asset than a service. The fiber itself must be maintained and repaired when there are problems like fiber cuts, and these outages are typically much longer than other services, so you should be careful to negotiate acceptable SLAs for these repairs. Long-haul dark fiber, in particular, is complicated because it requires optical regeneration or amplification. This means you have to figure out how to remotely monitor and maintain that equipment, which, depending on the route, could be in far-off and difficult to access locations. Of course, cost might be the concern of utilizing a dark fiber solution. Dark fiber generally costs more upfront capital expense due to the fiber infrastructure providers’ payment terms and additional equipment required. However, in most cases the long-term costs of a dark fiber solution may be much less than a long-term managed solution.
Ultimately, whether to employ a dark fiber solution is subject to review based on several factors. Operators must decide what solution will serve their end consumers best interests while meeting their own capacity needs.
Conclusion
To sum up, dark fiber can be the right solution for many of today’s high-bandwidth enterprise connectivity, but make sure you go into it with a full understanding of its advantages and disadvantages. FS.COM currently does not supply dark fiber services, but we are always committed to provide the first-class optical solutions to customers. Our optical cables are provided at lower price and high quality, such as SC FC patch cord, SC fiber patch cord, SC fiber patch cable and so on.
评论
发表评论